Setting the standard for MRD testing
Signatera™ is a highly sensitive and tumor-informed molecular residual disease assay (MRD) using circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), custom designed for each patient to help inform meaningful intervention.
The most comprehensively validated and widely used MRD assay available
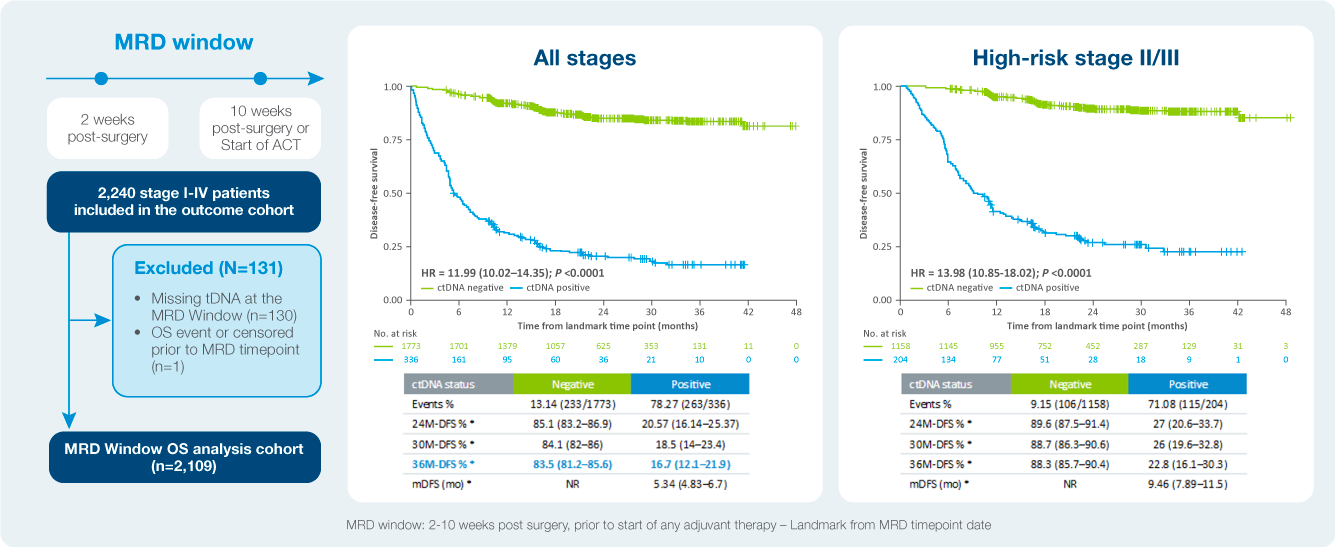
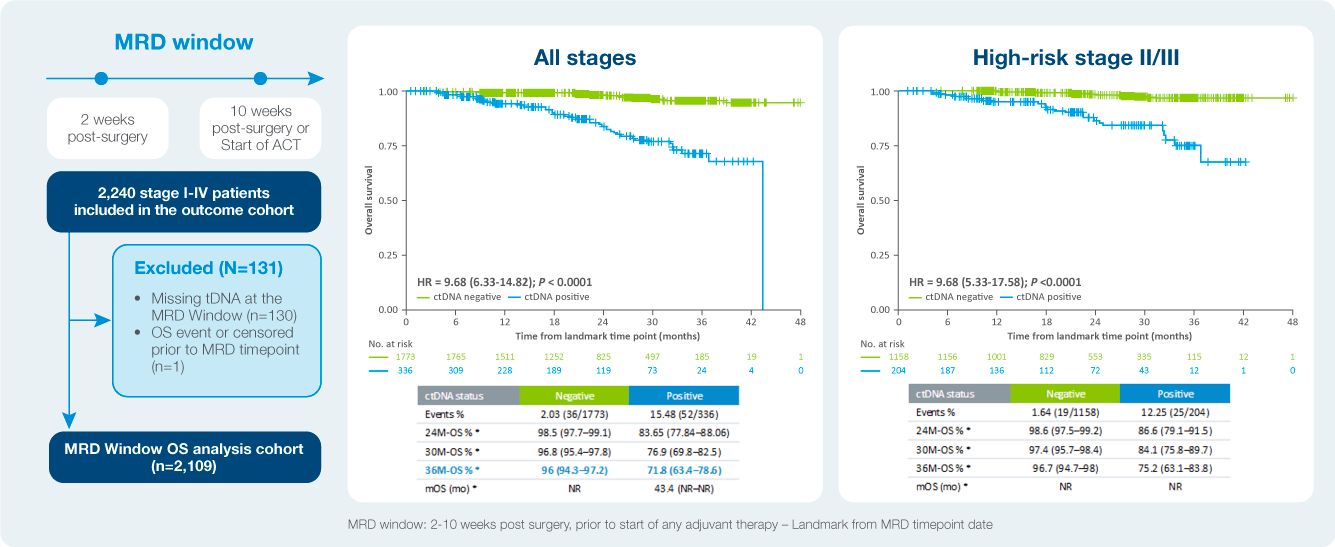
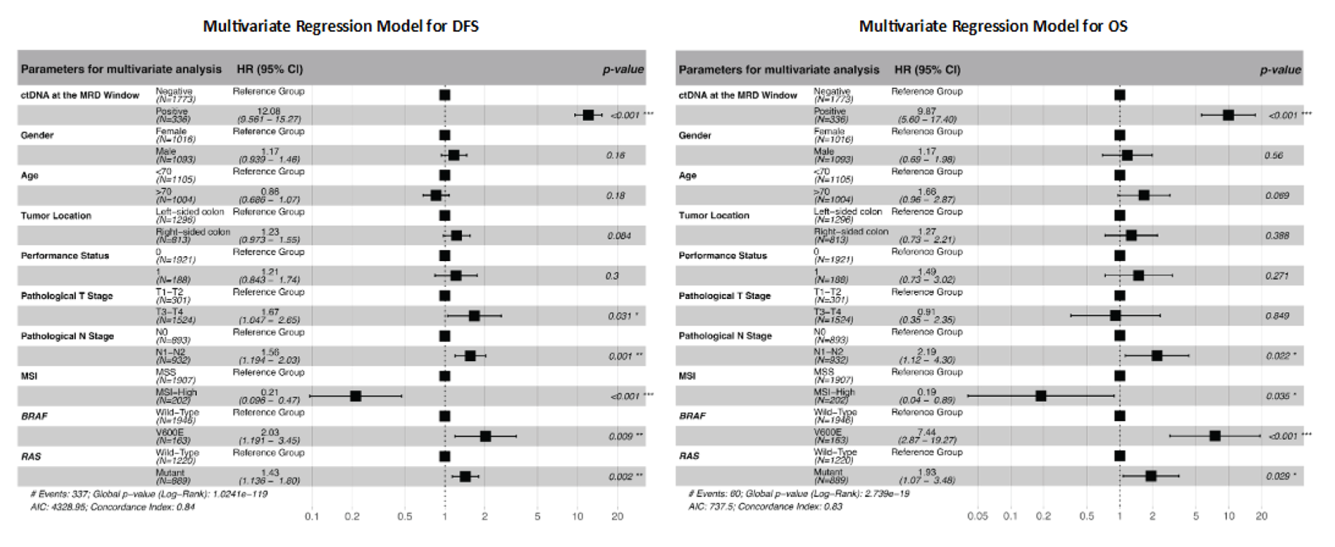
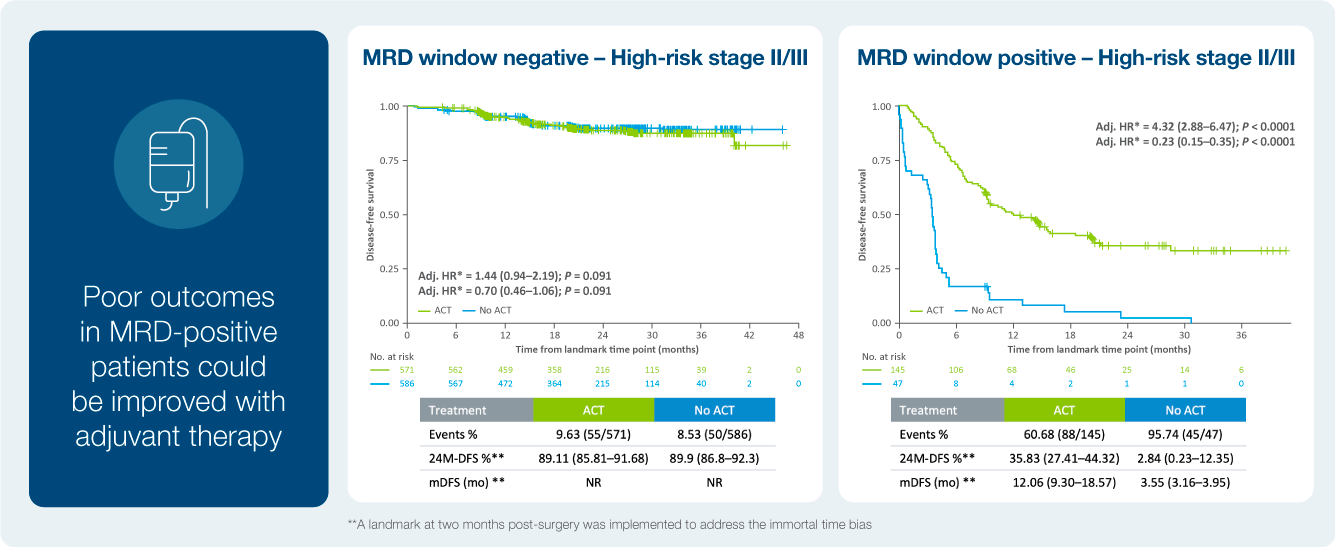
Identify patient at a high risk of recurrence
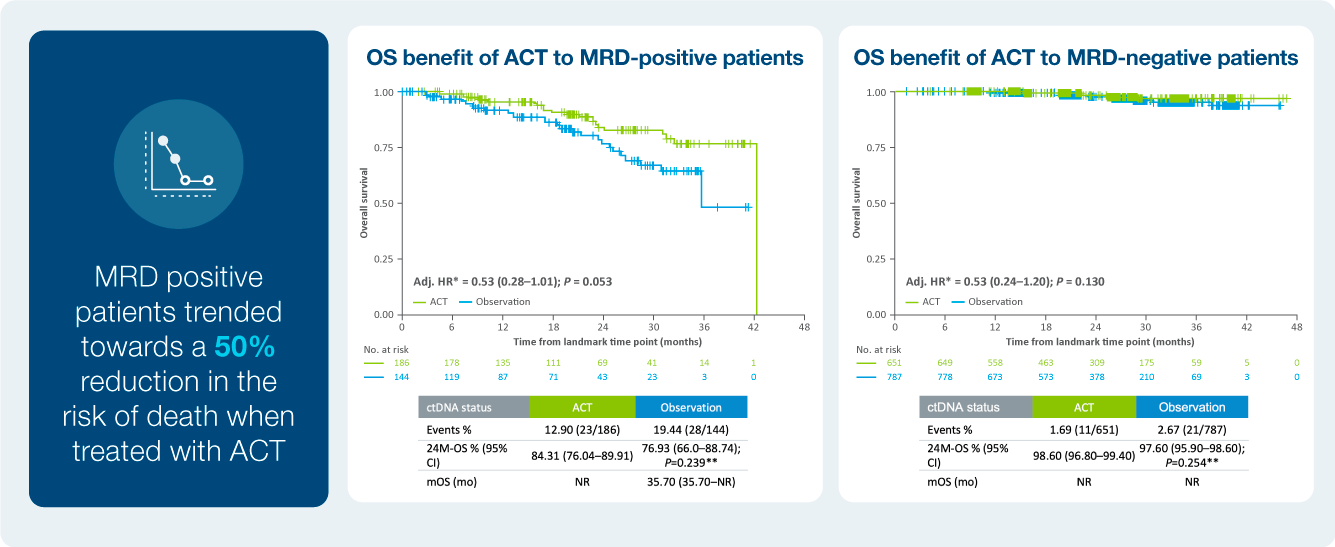
Treatment benefit in ctDNA positive patients
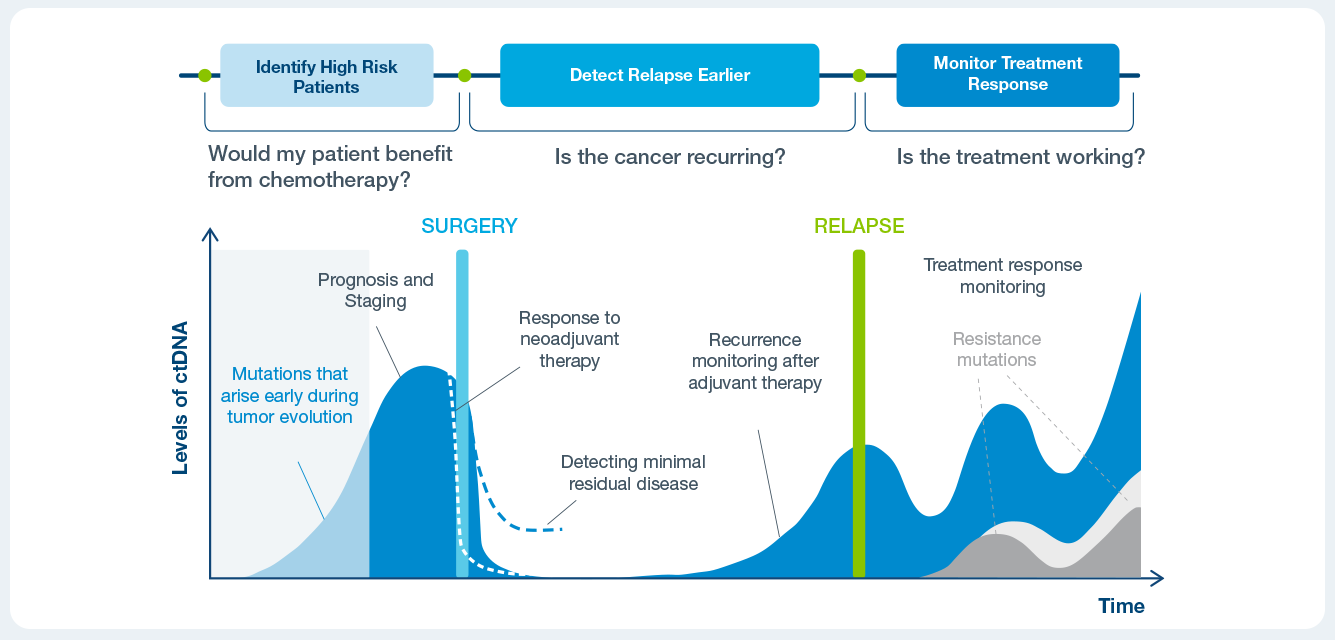
Informing treatment decisions along the continuum of care

Use Signatera™ after surgery to evaluate the need for adjuvant chemotherapy.
Use Signatera™ alongside CEA and imaging to detect recurrence earlier.

Assess a patient’s response to treatment in the neoadjuvant, adjuvant or immunotherapy settings.

Identify high risk patients with progressive disease who may benefit from earlier intervention or additional imaging.
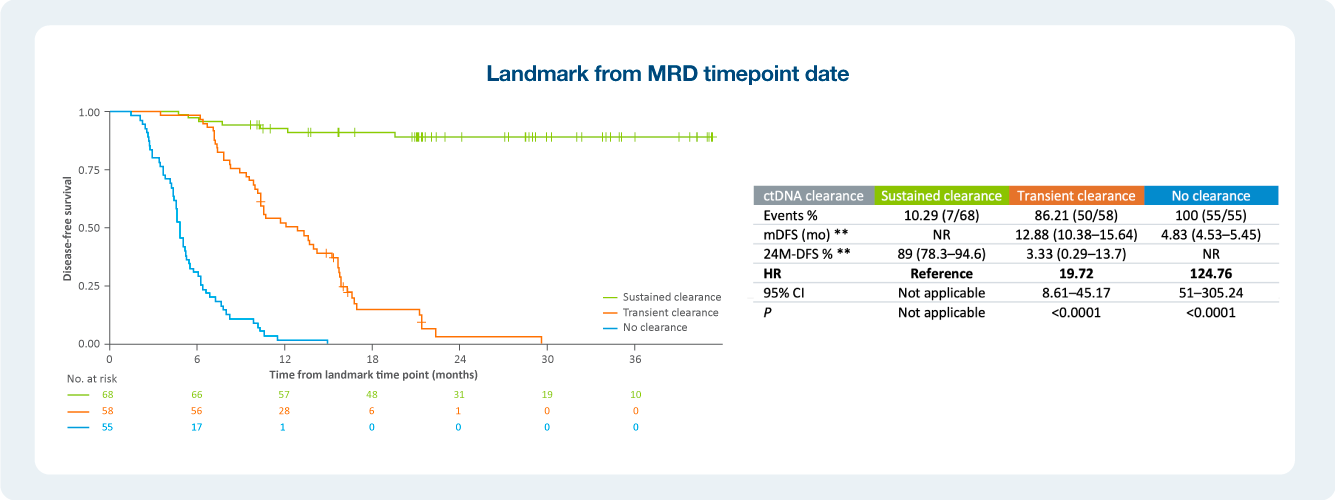
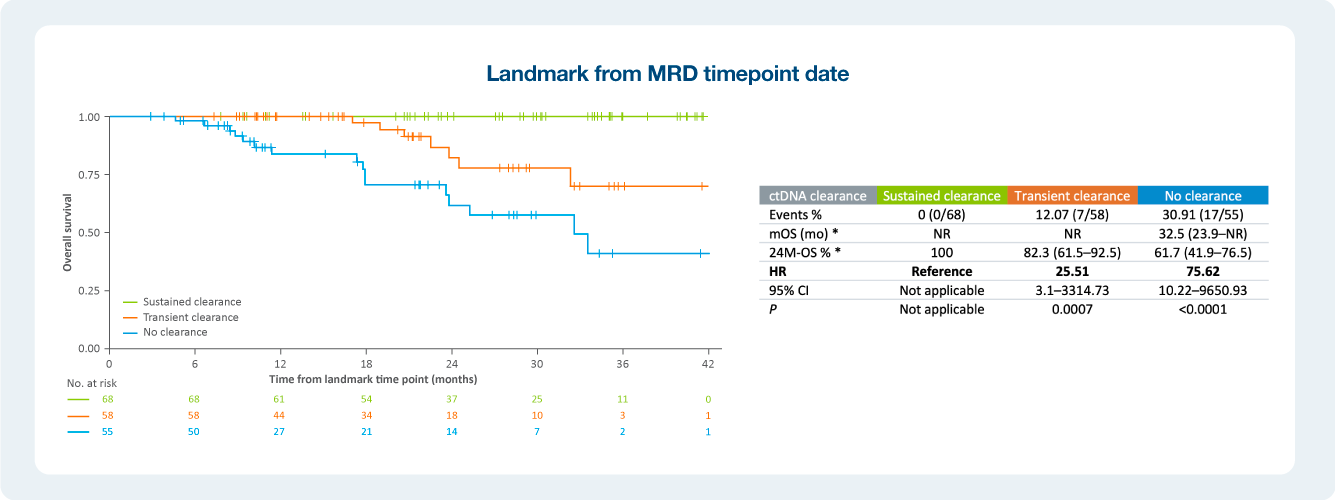
Impact of ctDNA clearance in Signatera positive patients
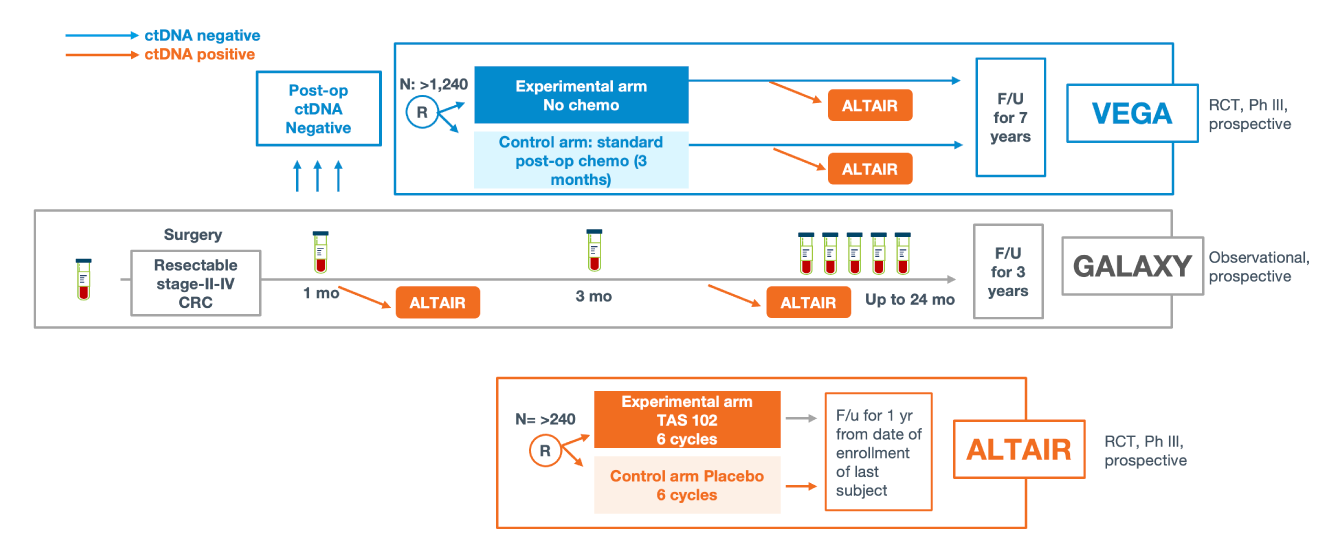
Clinical Application
The value of serial testing in the surveillance setting ctDNA status during surveillance was significantly associated with DFS
Clinical applications of ctDNA testing
Fine tuning chemotherapy
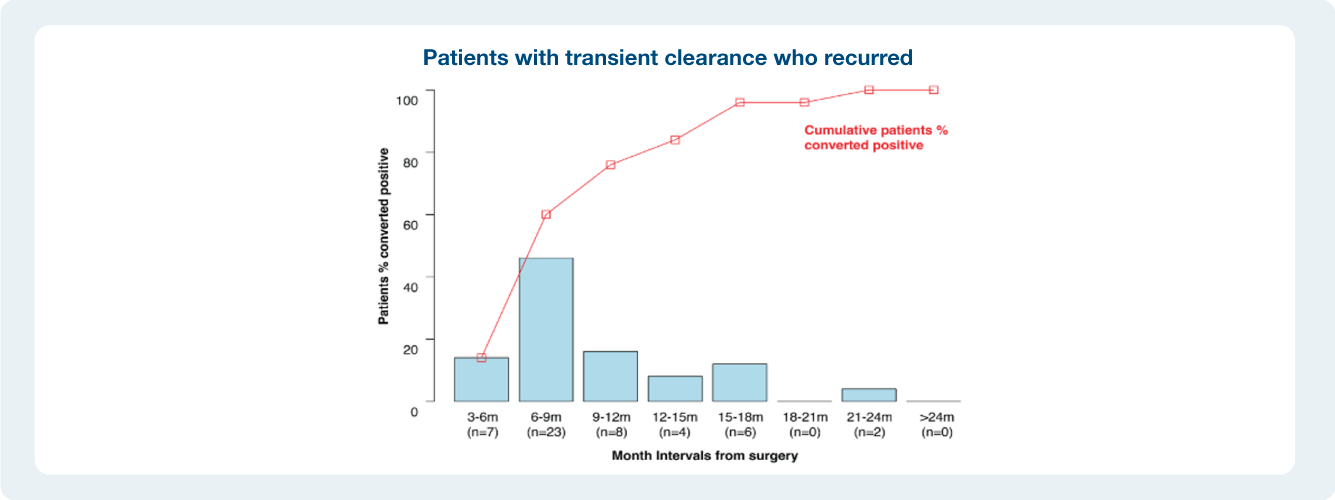
As we have seen in the recently presented data, patients who do not clear their ctDNA are at an increased risk of recurrence. Listen in how one providers incorporates Signatera™ into to his practice with the goal to impact patient care.
Tracks Disease Burden Over Time via ctDNA Dynamics
- Signatera™ is designed to accurately detect residual disease with an ultra-low level of detection
- Real time ctDNA analysis can help inform important adjuvant therapy decisions
- Signatera™ can also track ctDNA dynamics so you can gain real-time insight of disease burden.
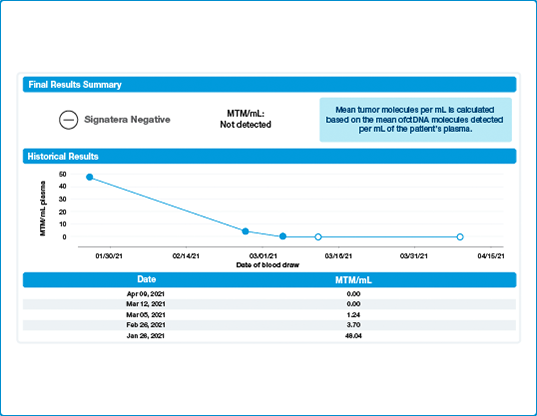
Facilitating shared-decision making
Listen in to Keith’s incredible story about how he and his provider used Signatera™ to help inform next steps in his treatment journey.
Is Signatera right for your patients?
We’re here to help you find out
References
1Reinert T, Henriksen TV, Christensen E, et al. Analysis of Plasma Cell-Free DNA by Ultradeep Sequencing in Patients With Stages I to III Colorectal Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019.
2Coombes RC, Page K, Salari R, et al. Personalized Detection of Circulating Tumor DNA Antedates Breast Cancer Metastatic Recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25(14):4255-4263.
3Abbosh C, Birkbak NJ, Wilson GA, et al. Phylogenetic ctDNA analysis depicts early-stage lung cancer evolution. Nature. 2017;545(7655):446-451.
4Christensen E, Birkenkamp-Demtroder K, Sethi H, et al. Early Detection of Metastatic Relapse and Monitoring of Therapeutic Efficacy by Ultra-Deep Sequencing of Plasma Cell-Free DNA in Patients With Urothelial Bladder Carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(18):1547-1557.
5Kotani D. et al., Molecular residual disease and efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with colorectal cancer, Nature Medicine v29 Issue 1 Jan 2023