Assess Disease at the Molecular Level
Accelerate development with ultra-sensitive MRD, earlier insights and access to unique biomarker defined populations.
Ultra-Sensitive MRD
Sequence tumor tissue and matched normal blood to identify tumor-specific genomic signatures

CGP & Biomarker Assays
Create custom multiplex PCR assay to target patient-specific clonal mutations in plasma
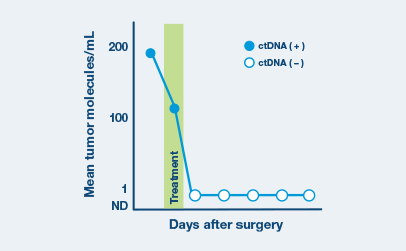
Real-world Data
Assess ctDNA levels over time to evaluate disease persistence, recurrence, and treatment response
Natera Acquires Foresight Diagnostics
This acquisition expands Natera’s lead in solid tumor MRD, bringing phased-variant MRD technology with detection below 0.1 ppm into the Signatera™ platform for immediate use in biopharma research and translational studies.
Partners can now leverage Natera’s unrivaled commercial, operational, clinical development infrastructure in MRD and Foresight’s unique phased variant technology and leadership in Hematology and Lymphoma.
Ultra-Sensitive MRD assays for comprehensive molecular insights
From market-leading to continued innovation: tumor-informed & tissue-free assays for all trial needs
- Most extensively validated, adopted, and reimbursed MRD assay with leading clinical perfomance10
- Ultrasensitive detection down to single digit PPM10
- Incorporates phased variants and structural variants for detection below 0.1ppm10
- Backed by Natera's extensive commercial & operational infrastructure10
- Epigenomic assay with fast turnaround time for when tissue is absent10
- Quantitatively validated for treatment response monitoring10
What is molecular disease and MRD?
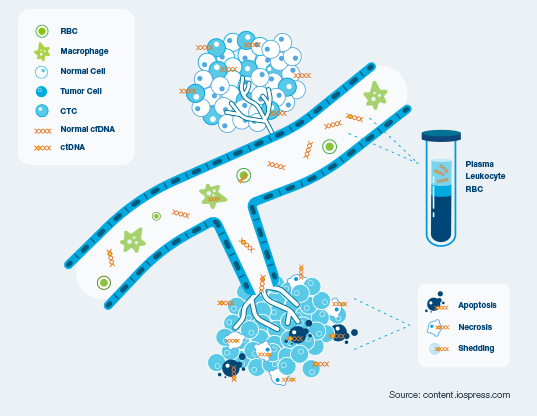
Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) is shed from cancer cells into the bloodstream. These tumor DNA fragments can be identified by Natera’s ultrasensitive ctDNA assays, offering an early quantitative, non-invasive approach to assess treatment response and disease progression.
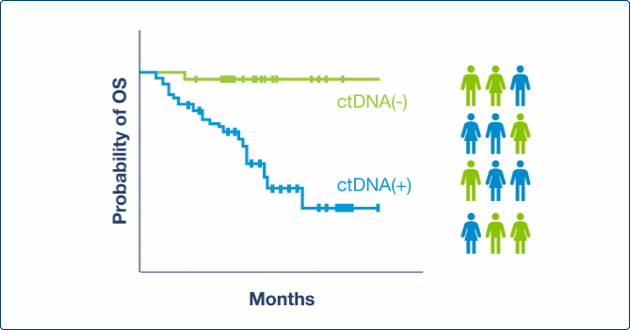
Across multiple studies, detection of molecular disease by Signatera™ was one of the most significant prognostic risk factors for recurrence3,6-9
Accelerate development with earlier insights and access to unique biomarker-defined populations
- Broader Populations: Expand intent to treat populations with biomarker stratification options
- Differentiated trial strategies: Multimodal biomarker insights to predict relapse risk and treatment response. Identify and enrich these high-risk patients to unlock new trial strategies
Enrich for High Risk Populations
- Stratify & enrich for study participants most likely to benefit from additional treatment1-2
- Treat on molecular relapse at time of lower disease burden
Benefits
- Maximize therapy efficacy and decrease necessary study size
- Move ahead of next-line therapies
Predict Response Sooner
- Predict therapy response as early as 6 weeks3 into treatment
- Support early therapy efficacy readouts as a co-primary or surrogate endpoint
Benefits
- Improve program prioritization and planning
- Accelerate approval of new therapies
Learn About MRD Data for Each Use Case
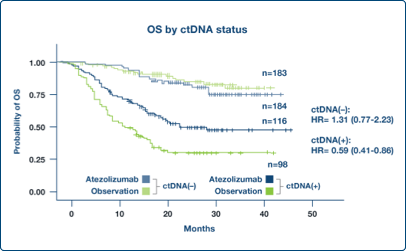
Enrich Populations
Post-surgical ctDNA status identified study participants who benefited from an investigational adjuvant therapy1
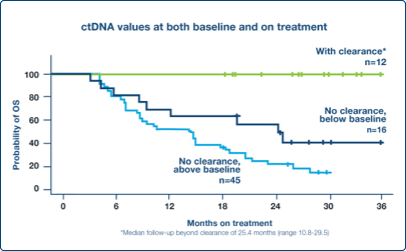
Monitor Response
Early decrease in ctDNA levels at week 6 correlated with favorable outcomes in the metastatic setting3
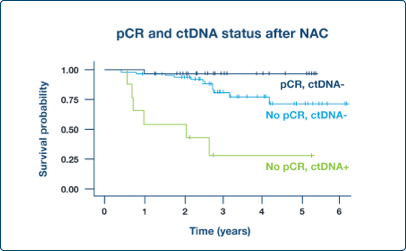
Supplement Endpoints
ctDNA dynamics in neoadjuvant setting can potentially support pathologic complete response (pCR) as surrogate endpoint4

Not all MRD tests are created equal
Signatera™ is the most comprehensive MRD test available. Review our peer-reviewed publications here.




How can Signatera™ support your clinical trials?
Contact us to learn more
References
1Powles T, et al. ctDNA guiding adjuvant immunotherapy in urothelial carcinoma. Nature. 2021;595:432–437. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03642-9.
2Oki E, Shirasu H, Watanabe J, et al. Dynamics of circulating tumor DNA after resection of colorectal cancer: Galaxy study in Circulate-Japan. Oral presentation presented at SSO, Dallas, Texas. March 9–12, 2022.
3Bratman SV, et al. Personalized circulating tumor DNA analysis as a predictive biomarker in solid tumor patients treated with pembrolizumab. Nature Cancer. 2020;1:873–881. DOI: 10.1038/s43018-020-0096-5.
4Magbanua MJM, et al. Circulating tumor DNA in neoadjuvant treated breast cancer reflects response and survival. Annals of Oncology. 2021;32(2):229–239. DOI: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.11.007.
5Shoushtari A, Collins L, Arranz E, et al. Early reduction in ctDNA, regardless of best RECIST response, is associated with overall survival (OS) on tebentafusp in previously treated metastatic uveal melanoma (mUM) patients. Oral presentation presented at ESMO GI. September 16–21, 2021. Abstract ID: 3600.
6Kotani D, et al. Molecular residual disease and efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with colorectal cancer. Nature Medicine. 2023.
7Yukami H, Nakamura Y, Mishima S, et al. Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) dynamics in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients with molecular residual disease: Updated analysis from GALAXY study in the CIRCULATE-JAPAN. Oral presentation presented at ASCO Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium, San Francisco, CA. January 18–20, 2024.
8Magbanua MJM, Swigart LB, Ahmed Z, et al. Clinical significance and biology of circulating tumor DNA in high-risk early-stage HER2-negative breast cancer receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer Cell. 2023;41(6):1091–1102.
9Huffman BM, Aushev VN, Budde GL, et al. Analysis of circulating tumor DNA to predict risk of recurrence in patients with esophageal and gastric cancers. JCO Precision Oncology. 2022;6:e2200420.
10Natera. Publicly reported and internal data as of January 2026.
11Final Local Determination Coverage for stage II and III CRC, stage IV oligometastatic CRC, surveillance monitoring in Stage I–III NSCLC, neoadjuvant, adjuvant, and recurrence monitoring for muscle-invasive bladder cancer, adjuvant and surveillance monitoring for locally and regionally advanced breast cancer, neoadjuvant treatment response monitoring for stage II–IV breast cancer, adjuvant and surveillance monitoring for ovarian cancer, and pan-tumor IO monitoring.
12Total patients enrolled or to be enrolled in ongoing trials prospectively using Signatera™ for risk stratification, enrichment, and/or treatment response monitoring.