Now Available: Prospera™ Heart for Pediatrics
Learn MoreNow Available: Prospera™ Heart for Pediatrics
Learn MoreProspera™ Heart with DQS
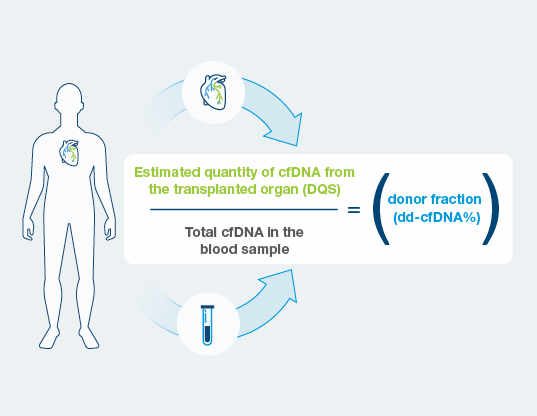
Extensive history and experience with cell-free DNA across industries powers new innovative features including a proprietary technique to estimate both the quantity and the fraction (dd-cfDNA %) of donor derived cell-free DNA in a single blood test.
Introducing Donor Quantity Score (DQS) to the Prospera™ Heart test for a clearer picture of rejection risk
Traditional dd-cfDNA tests
- Detect DNA in the blood from the donor heart and reports this as a fraction of the total cell-free DNA in the blood.
- The fraction of dd-cfDNA may be impacted when the amount of total cell-free DNA is atypically high or low.
DQS is the next evolution of dd-cfDNA results
- DQS is the estimated quantity of cell-free DNA coming from the donated heart.
- Unlike traditional dd-cfDNA tests, DQS is independent of fluctuations in levels of total cell-free DNA in the blood.
Celebrating one year with Prospera™ Heart with DQS
The next evolution of dd-cfDNA rejection monitoring
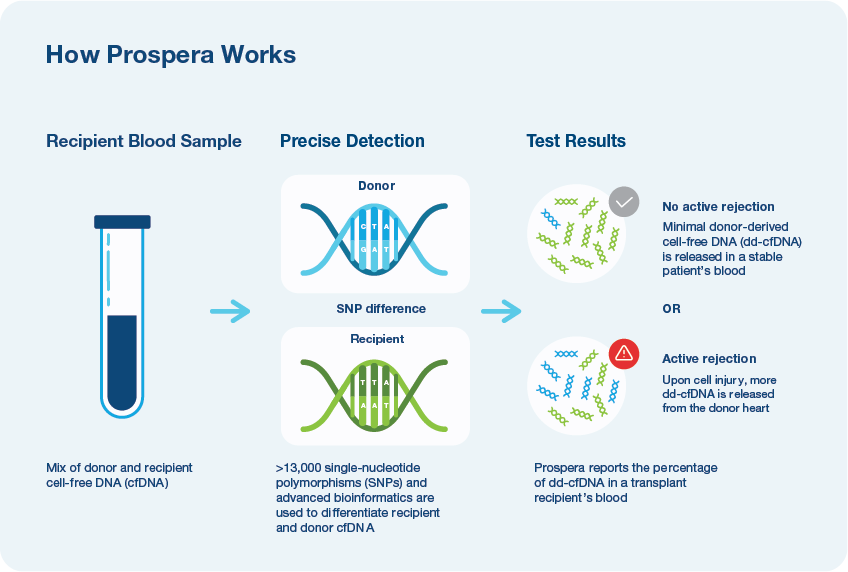
- Developed by Natera, a leader in cell-free DNA (cfDNA) with a trusted legacy in fetal monitoring, oncology and organ health
- Demonstrated in over 10 million tests1
- Utilizes over 13,000 pan-ethnic SNPs and advanced bioinformatics2
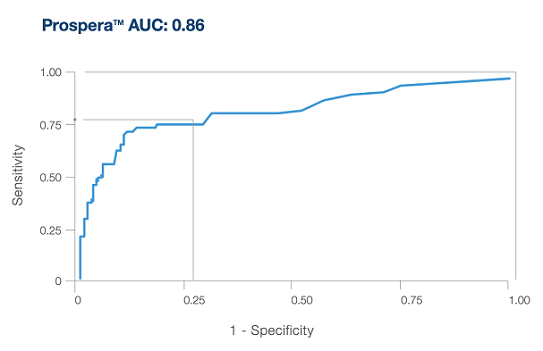
- Only Prospera™ Heart with DQS provides two donor derived cell-free DNA metrics and has been shown to improve accuracy in screening for acute cellular rejection (ACR) and antibody mediated rejection (AMR).3
Brief video to learn more about Prospera™ Heart with DQS
ISHLT Symposium Presented by Natera
This session highlights the exciting new data in support of noninvasively monitoring for rejection risk post heart transplantation. The addition of a second threshold called Donor Quantity Score (DQS) has been shown to improve the overall performance of the test and reduce false positive rates by 37%8 compared to dd-cfDNA fraction % alone. The session will provide an overview of literature in support of the DQS metric as well as share personal clinical accounts in the form of case studies to highlight its value in supporting clinical decision making.
Hear from these speakers:
- Michael Olymbios, MD, Natera, San Carlos, CA USA
- Philip Halloran, MD, PhD, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB Canada
- Brent Lampert, DO, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH USA
- Roopa Rao, MD, Indiana University Health, Indianapolis, IN USA

ISHLT Industry Symposium
Two Thresholds, One Powerful Solution:
Enhancing Overall dd-cfDNA Testing Accuracy in Heart Transplantation Using Fraction and Donor Quantity Score (DQS)
60 minute symposium with Q&A
“There is a need for a sensitive, noninvasive surveillance tool for early detection of transplant injury to reduce frequency of biopsy in heart transplantation.”6
Why Prospera?
The current surveillance landscape has limitations and the management of heart transplant recipients is complex and challenging
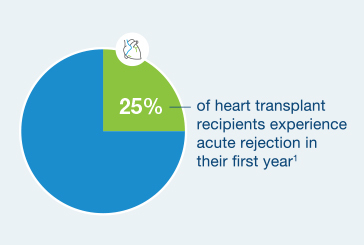
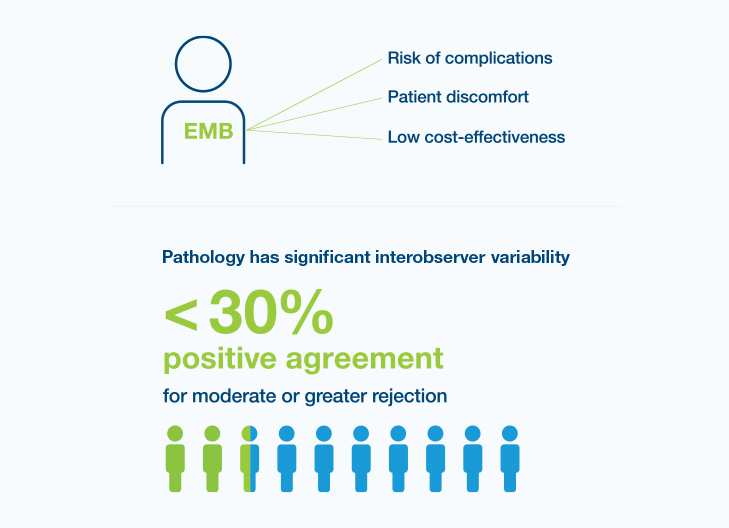
25% of heart transplant recipients experience acute rejection in their first year4
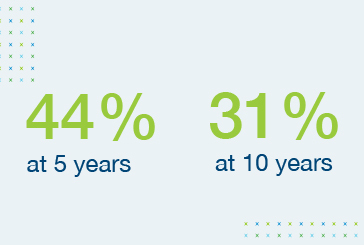
Survival rates of heart transplant recipients show little improvement over time5

Though endomyocardial biopsy (EMB) is the gold standard in surveillance for acute rejection, it has recognized challenges
Precision optimized for enhanced performance
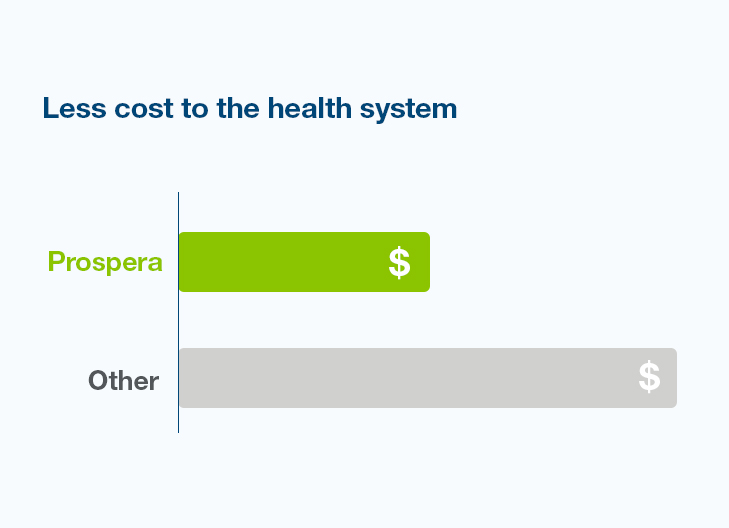
Reduce the number of surveillance biopsies by using Prospera as your first-line surveillance test
Patients first, partners always
Natera’s suite of solutions allows for streamlined process integration for your center

Total EMRSync
A complete, secure bi-directional data and workflow interface with Epic and Cerner systems
- Allows for easy ordering and delivery of results

ProsperaLink Program
A concierge team of clinical experts including a medical science liaison, nurse coordinator, & patient coordinator to help patients stay updated on blood draws, compliance plans and results.

Financial Support Program
- Natera welcomes all insurances, and our goal is to make the process easy and transparent for patients
- In the rare event your patient has financial responsibility, Natera offers flexible financial assistance programs and will work closely with your patient to ensure there is no hardship on them or their family.
Find out more about Prospera for heart transplant recipients
References
1Natera Inc. Natera validation data: manuscript submitted. Data on file.
2Sigdel TK, Archila FA, Constantin T, et al. Optimizing detection of kidney transplant injury by assessment of donor-derived cell-free DNA via massively multiplex PCR. J Clin Med. 2018;8(1):19. doi:10.3390/jcm8010019
3Kim P, et al. A Two-Threshold dd-cfDNA Algorithm for Detection of Rejection After Heart Transplant. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2024;43(4):S205-S206.
4U.S. Department of Health & Human Services: Health Resources and Services Administration. Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients (SRTR): Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN)/SRTR 2019 Annual Data Report: Heart. Available at: https://srtr.transplant.hrsa.gov/annual_reports/2019/Heart.aspx#HR_tx_adult_inc_AR_age_b64. Accessed June 1, 2021.
5Altug Y, Liang N, Ram R, et al. Analytical validation of a single-nucleotide polymorphism-based donor-derived cell-free DNA assay for detecting rejection in kidney transplant patients. Transplantation. 2019;103(12):2657-2665. doi:10.1097/TP.0000000000002665
6Toyoda Y, Toyoda Y. Heart-lung transplantation: adult indications and outcomes. J Thorac Dis. 2014;6(8):1138-1142. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2014.06.01
7Kim PJ, Olymbios M, Siu A, et al. A novel donor-derived cell-free DNA assay for the detection of acute rejection in heart transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2022. doi:10.1016/j.healun.2022.04.002
8Kim PJ, Olympios M, Sideris K, et al. A Two-Threshold Algorithm using Donor-derived Cell-free DNA Fraction and Quantity to Detect Acute Rejection After Heart Transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2025. doi:10.1016/j.ajt.2025.04.021.